
Advertisement
In this article, you can check out the syllabus for class 12 ECONOMICS – PSEB (For 2023-24) and you can also download the syllabus in the PDF Format.
CLASS-XII – 2023-24 ECONOMICS (COMMERCE and HUMANITIES GROUP)
INA/Project work:20Marks and Total: 100 Marks
Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics
Unit 1: National Income and Related Aggregates
What is Macro Economics? Classical and Keynesian views about Macro Economics. Scope, Importance and Limitations of Macro Economics. Concept of Equilibrium: Partial Equilibrium and General Equilibrium. Basic concepts in Macro Economics: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods, intermediate goods, stock and flow variables, etc.
Circular flow of income and output (two sector economy model). Real flow and Monetary flow. Concept of Injections and withdrawals in Circular flow of Income and Output. Aggregates related to National Income: Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross and Net Domestic Product (GDP and NDP) – at market price, at factor cost. Methods of calculating National Income – Value Added or Product method, Expenditure method, Income method with numerical questions.
Unit 2: Determination of Income and Employment
Aggregate Demand- Aggregate Supply and their components. Consumption function, Saving function, Investment function. Propensity to consume and propensity to save (average and marginal). Short-run equilibrium output. Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment.
Investment multiplier and its mechanism.
Advertisement
Problems of excess demand and deficient demand.
Measures to correct excess and deficient demand through Monetary and Fiscal policies of the government along with the instruments of monetary and fiscal policies.
Unit 3: Money and Banking
Money – Barter System of Exchange: Meaning and Limitations. Money: Meaning, types, Importance, Functions of Money, advantages and disadvantages of money. Concept of Supply of Money and its measurement.
Banking: Meaning and Functions of Commercial Banks. Meaning and functions of Central bank (example of the Reserve Bank of India). Control of Credit by Central Bank through quantitative and qualitative measures.
Unit 4: Government Budget and the Economy
Government Budget – meaning, objectives and components. Classification of receipts – revenue receipts and capital receipts; tax: meaning and types of taxes; classification of expenditure – revenue expenditure and capital expenditure, planned expenditure and non-planned expenditure, developmental and non-developmental expenditure.
Advertisement
Measures of government budget deficit – revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit their meaning and measurement.
Unit 5: Foreign Exchange Rate and Balance of Payments
Foreign exchange rate – Meaning of fixed and flexible exchange rates and methods of their determination along with their advantages and limitations. Foreign Exchange market-Meaning, types and Functions.
Balance of Payments- Meaning and components. Various types of accounts in Balance of Payment. Deficit in Balance of Payment: Meaning, causes and measures to correct it.
Part B: Indian Economic Development
Unit 6: Development Experience (1947-90) and Economic Reforms since 1991
A brief introduction of the state of Indian economy on the eve of independence.
Five Year Plans and NITI Aayog; Rational behind the adoption of five years economic plans, common goals of five-year economic plans with their success and failures. NITI AAYOG; A brief introduction, structure, objectives and its working.
Advertisement
Agriculture: Meaning, Importance, main features, problems and policies of agriculture (institutional aspects and new agricultural strategy).
Industry: Meaning, Importance, problems and policies for industrial development (industrial licensing, etc.).
Economic Reforms since 1991: Features of Liberalisation, Privatization and Globalisation (LPG policy) and measures adopted in this policy of LPG. A critical evaluation of LPG Policy.
Unit 7: Current challenges faced by Indian Economy
Poverty- absolute and relative. Causes of Poverty, suggestions to solve the problem of poverty from India and main programs for poverty alleviation: A critical assessment. Unemployment: Meaning, types and causes, suggestions to solve the problem of unemployment from India. Main programs for the solution of the problem of unemployment from India.
Rural development: Key issues – rural credit and rural marketing – role of cooperatives; agricultural diversification; – organic farming.
Human Capital Formation: Meaning, how people become human capital; Role of human capital in economic development; Growth of Education Sector in India.
Infrastructure: Meaning and Types: Energy and Health: Problems and Policies: A critical assessment.
Sustainable Economic Development: Meaning, Effects of Economic Development on Resources and Environment, including global warming. Concept of Pollution: Types and suggestions to solve the problem of pollution.
Part C: Statistics in Economics
Unit 8: Correlation and Index Numbers
Coefficient of Correlation – meaning and properties. Methods for the measurement of coefficient of correlation: scatter diagram method, Karl Pearson’s method (only by direct method) (two variables ungrouped data) Spearman’s rank order correlation (in case of untied ranks only).
Index Numbers – Meaning, objectives, problems in the construction of index numbers, methods of constructing; Unweighted Index (Simple aggregative and simple average of price relative method). Weighted Index Numbers (Weighted aggregative methods including Laspeyre’s, Pasche’s and Fisher’s Index Numbers). Wholesale price index, Consumer price
index and index of industrial production. Uses of index numbers; Inflation and index numbers.
Developing Project in Economics
The students may be encouraged to develop projects, as per the suggested project guidelines. Case studies of a few Organisations/outlets may also be encouraged. Under this, the students will do only ONE comprehensive project using concepts from Part A, B and C of their syllabus.
Guidelines for Project Work in Economics
The objectives of the project work are to enable learners to:
Probe deeper into theoretical concepts learnt in XII
Analyse and evaluate real world economic scenarios using theoretical constructs and arguments
Demonstrate the learning of economic theory
Follow up aspects of economics in which learners have interest
Develop the communication skills to argue Logically
The expectations of the project work are that:
Learners will complete ONE project and will work on one topic off Moral Values and try to imbibe those values along with the Project Work in each academic session.
Project should be of 1000 words (excluding diagrams & graphs), preferably hand-written
It will be an independent, self-directed piece of study
Role of the teacher
The teacher plays a critical role in developing thinking skills of the learners. A teacher should:
Help each learner select the topic based on recently published extracts from the news media, government policies, RBI bulletin, NITI Aayog reports, IMF/World Bank reports etc., after detailed discussions and deliberations of the topic.
Play the role of a facilitator and supervisor to monitor the project work of the learner through periodic discussions
Guide the research work in terms of sources for the relevant data.
Educate learner about plagiarism and the importance of quoting the source of the information to ensure authenticity of research work
Prepare the learner for the presentation of the project work Arrange a presentation of the project file
Scope of the project
Learners may work upon the following lines as a suggested flow chart:
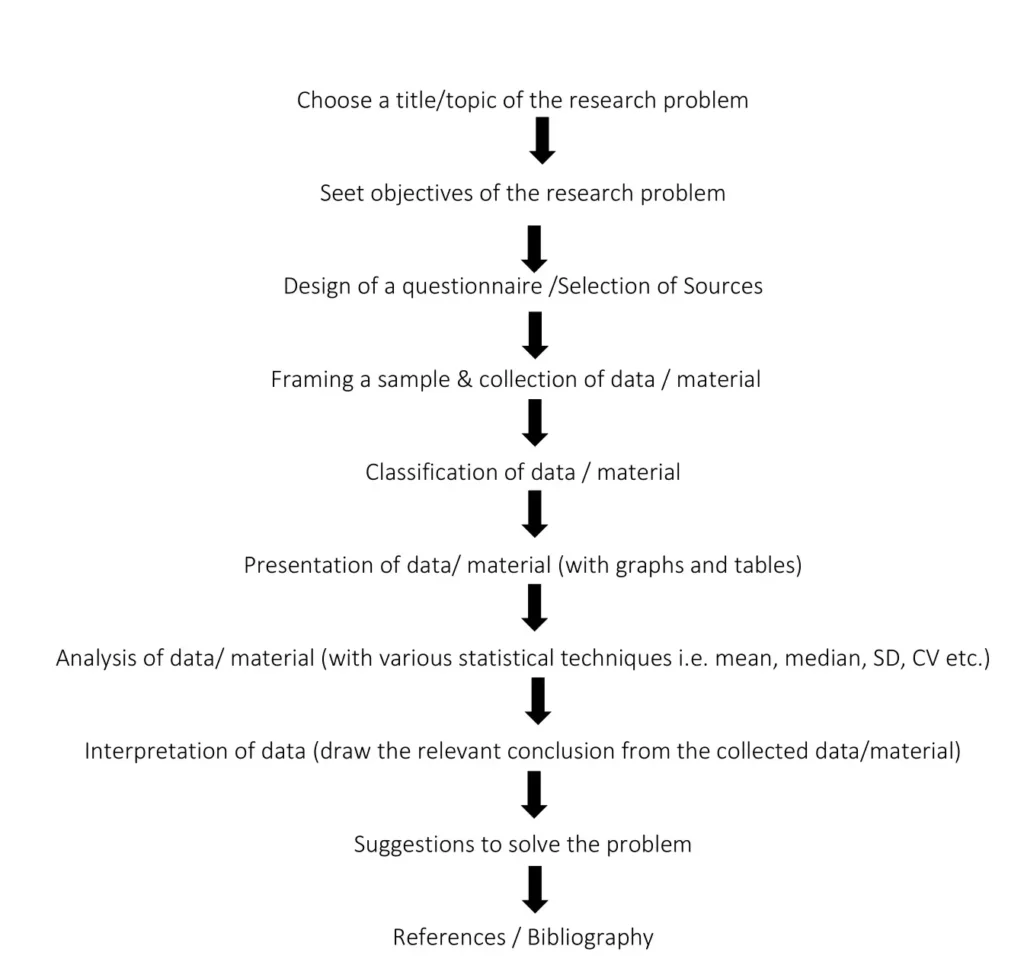
Expected Checklist
- Introduction of topic/title Identifying the causes, consequences and/or remedies
- Various stakeholders and effect on each of them
- Advantages and disadvantages of situations or issues identified
- Short-term and long-term implications of economic strategies suggested in the course of research.
- Validity, reliability, appropriateness and relevance of data used for research work and for presentation in the project file.
- Presentation and writing that is succinct and coherent in project file
- Citation of the materials referred to, in the file in footnotes, resources section, bibliography etc.
Mode of presentation/submission of the Project
At the end of the stipulated term, each student will present the research work in the Project File to the External and Internal examiner. The questions should be asked from the Research Work/ Project File of the learner through viva-voce. The Internal Exam inner should ensure that the research report submitted by the learner is his/her own original work. In case of any doubt, authenticity should be checked and verified.
Some of the examples of the projects are as follows (they are not mandatory but only suggestive):
- Goods and Services Tax and its impact on GDP
- A critical analysis of the present year Government Budget
- Determination of Minimum Support Prices in India
- Digital India- A step towards the future
- Role of RBI in Controlling Money Supply in India
- Health Expenditure in India- A comparison of two or more states can be done
Moral Value Topics:
- Sarv Shiksha Abhiyan- Cost-benefit Analysis
- Waste Management- A Need of the Hour
- Make in India- The way ahead
- Rainwater harvesting- A solution to the water problem in India
- Organic Farming- Back to the nature
Download syllabus for class 12 ECONOMICS – PSEB in PDF
Download the PDF of the Syllabus for Class 12 BUSINESS STUDIES – II – PSEB For Free of cost
Check out Solutions of Various Books of Accountancy for Class 12 For PSEB
Punjab School Education Board (PSEB) Solutions of Usha Publication.
If you’re a student enrolled in the Punjab School Education Board Class 12, it’s essential to explore a wide range of books to cover the syllabus thoroughly. While the prescribed textbooks are undoubtedly valuable, supplementing your studies with additional resources can enhance your understanding and knowledge. Consider checking out other books that align with the curriculum, offering different perspectives and insights on the subjects you’re studying. These supplementary materials can provide you with alternative explanations, practice questions, and examples that may aid in clarifying complex concepts. Moreover, exploring diverse sources can expose you to a variety of writing styles and viewpoints, fostering a broader understanding of the subjects. So, seize the opportunity to expand your learning by delving into other books that can complement your studies and contribute to your academic growth.
Advertisement



